Parts of a flower and their functions pdf
Parts of a flower and their functions pdf
Anatomy of a Flower stigma catches pollen carpel (pistil) female part of a flower stamen male part of a flower anther produces pollen grains filament holds up the anther petal attracts insects and mammals to the flower for pollination style connects the stigma to the ovary ovary stores the ovule or ovules ovule contains the embryo sac receptacle the thickened part of a stem sepal protection
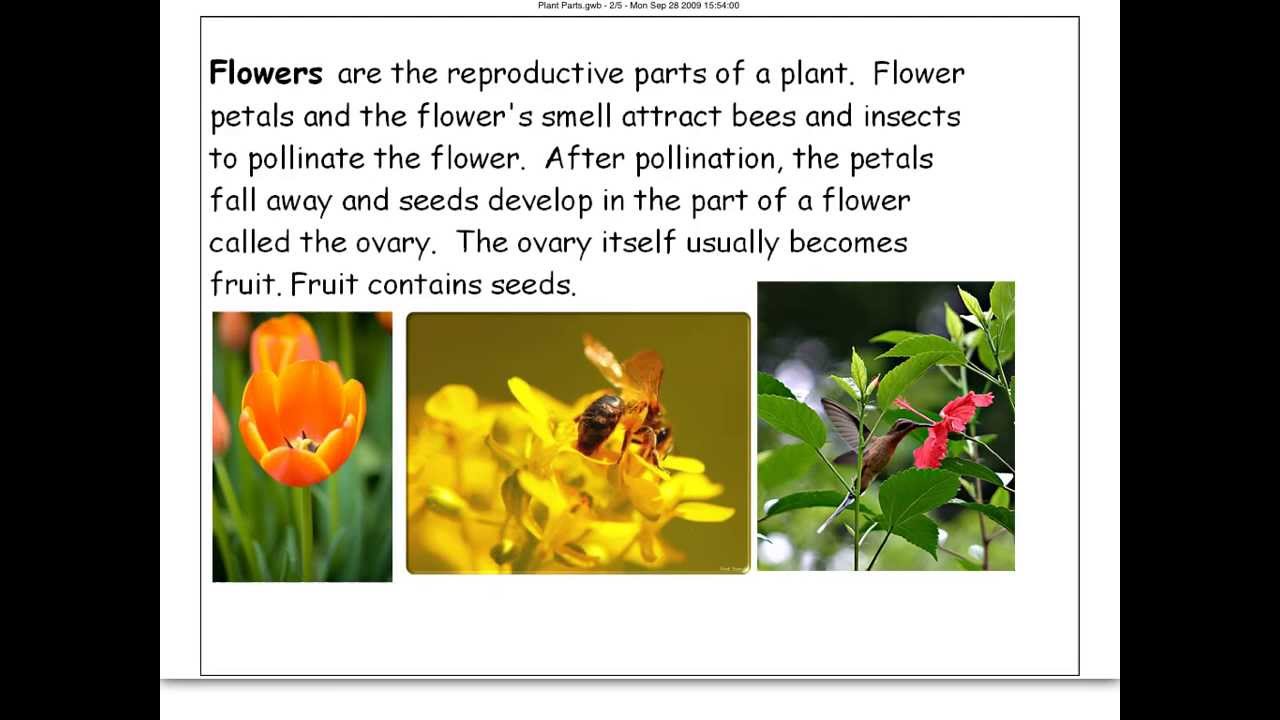
The flower has both female parts, called the pistil, and male parts, called the staemens. They work together to fertilize the plant and produce seeds. The petals of a flower attract other insects such as butterflies and bees to the plant to pollinate them.
The important parts of a flower and their specific functions have been listed in this article. The most important parts are its male and female parts, the carpel, and the stamen.
Day One: Distribute Parts of a Flower (Handout One). Ask the learners to label the parts of the plant with the appropriate name and function. Ask learners to share their prior knowledge of plants. Correct or enhance their understanding as necessary. During this discussion, the teacher can begin to state possible analogies of the parts of a plant to the parts in government. (constitution is
female parts of the flower, consisting of the stigma and the style
Flower Parts Worksheet. Label the flower using the words provided below. ANTHER STYLE FILAMENT NECTARY PETAL SEPAL OVARY STIGMA . 2 . 1 . 4 . 3 . 8 . 7 . 6 . 5 . Extra information. The female part of the flower is called the CARPEL or PISTIL. The ovary contains OVULES or eggs. The male part of the flower is called the STAMEN. It is made up of the anther that contains pollen, …
functions of parts of the flower and will learn to use these words in us with beauty and wonderful aromas, but what is their function in nature? The main role of the flower is to make seeds, and seeds become fruit. The flower is
4.8 : Reproductive System in Flowering Plants! Parts of the Flower & their Functions! • Bisexual flowers : Have both stamens (male) and pistils
27/12/2011 · flower: A modified and condensed shoot useful for reproduction in angiosperms is called flower. Famous scientists like Linnaeus, Gaspard Bauhin, Goethe, de Candolle described flower as a …
their function. • Pass out the real flower. Encourage the students to examine it with hand lenses and identify its parts and where the parts are found in the flower. Explain that they must handle the flower carefully so that it does not break apart. Have each student draw the flower in their journal, including all the parts. If drawing is difficult for the students, have an adult draw the
Functions and Parts of a Plant (PDF) – Have fun learning about the lifecycle of a plant, including how flowers form and their various parts. Guide to Flowers (PDF) – Check out this cool flower picture guide that you can use to identify different parts of a flower once you learn about basic plant anatomy!
GWS parts of a flower curriculum Groundwork Somerville

Four Whorls The Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
Flower Parts Strand Life parts and their functions. Extensions and Connections (for all students) If students used a digital camera to collect pictures of plants on the school grounds, the class book about plants could be produced electronically. Have students create a flip book with illustrations of the stages of pollination. Give four 3 x 5 inch index cards to each student, and have them
This ‘ideal’ flower shows the basic parts of a flower. Children need to recognise these parts in Children need to recognise these parts in different flowers and understand their role or function in flowering plant reproduction.
The flower is the organ of reproduction in flowering plants. The male part of the flower is the stamen (composed of the anther where pollen is made and the thin filament ). The female part of the flower is the pistil (composed of the stigma , the thin style and the ovary ).
The Functions of the Parts of a Flower. ANTHER Female part, sticky and collects the pollen. CARPEL Male part, holds up the anther. FILAMENT Female part, tube that the pollen travels down.
Identifies the basic plant parts Plant parts and functions Roots Structure – Tap root, lateral root, Root hairs, Grade 3 Life Science 4 Lesson 1 – Parts of a Plant Materials: Roots – strings of ropes that go around the ankles Stems – a belt of straws that goes around the waist Leaves – green paper leaves that go on the arms Flower – a flower that goes on the students head
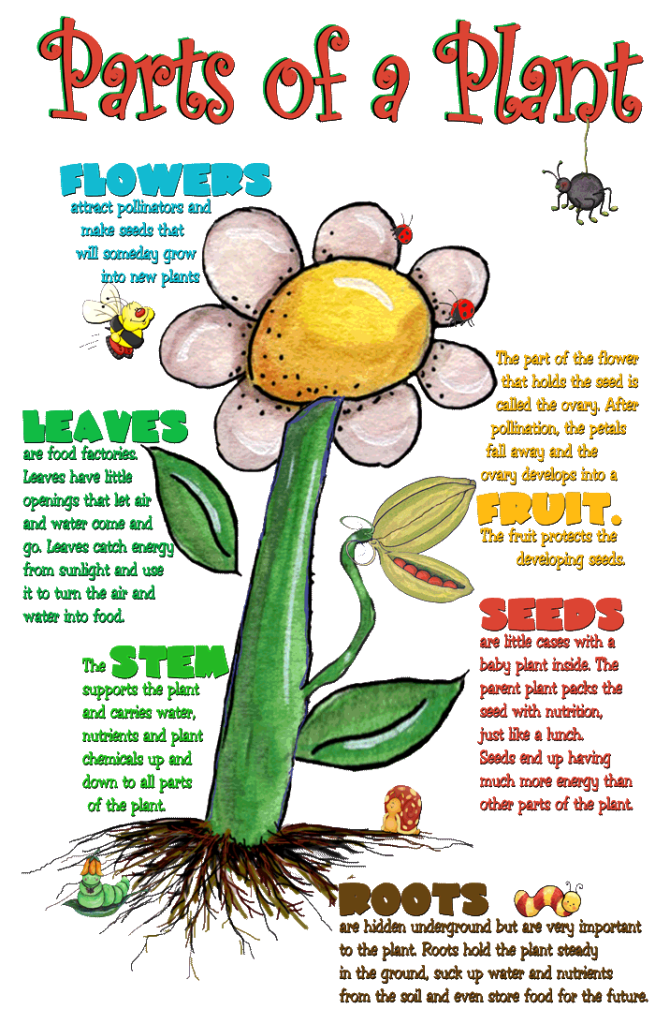
Their parts are called the root, stem, branch, leaf, flower, fruit, and seed. We learned that roots anchor the plant to take in their water and nutrients and hold the plant firmly in the ground. Roots are also absorbers of water and minerals from the soil.
The parts of a plant and their functions 1. The Parts of a Plant and their Functions By: Elisabeth D.S. Cecil Nur A. Irfan Fahrizza Risngo Nanny B. Clementinus Ken B.
All flowers have male and female parts carpel stamen This is the name for the FEMALE part of the flower. This is the name for the MALE part of the flower. This is the name for the MALE part of the flower.
Two other important parts are the pedicel, a stalk on which flowers are frequently borne, and the top of the pedicel, called the receptacle, to which the other flower parts are typically attached. Of the four main parts, the sepals are generally the most leaf like and …
Identifies the basic plant parts Plant parts and functions Roots Structure – Tap root, lateral root, Root hairs, Grade 3 Life Science 5 Lesson 2 – Flower Dissection Lab Objectives: • To learn the parts of the flower. • To compare male and female flower anatomy Materials: Flower paper towel plastic knife flower diagram Picture from www.madsci.org Procedure: 1. Each group will be given
The three primary parts of a seed are the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The embryo is the young multicellular organism before it emerges from the seed. The endosperm is a source of stored food, consisting primarily of starches. The seed coat consists of one or more protective layers that encase the seed. A seed begins to form an embryo following fertilization and the start of a zygote. The
Non-reproductive parts of a flower are known as the Perianth and consist of the petals, sepals and the nectary. Petals are usually the colored parts of the flower, although some flowers have specialized leaves called bracts that can be even more colorful than the flower itself.
Includes: – Parts of the Flower Flip Book – Flower Life Cycle Flip Book Kids can cut out and paste the different parts into their flip book.” “This flip book allows students to label the parts of a flower.
Science Curriculum Unit Planner SOL
Lesson One Rose Flower Anatomy Texas A&M University Rose Breeding and Genetics Program Lesson Series in Rose Hybridization. Objectives • Identify flower parts • Identify function of each floral part • Identify flower parts on a rose flower. The Flower Its significance to the rose breeder? ‘Tis the place where all new roses begin!*** ***And yes, a few of them are mighty pretty. An
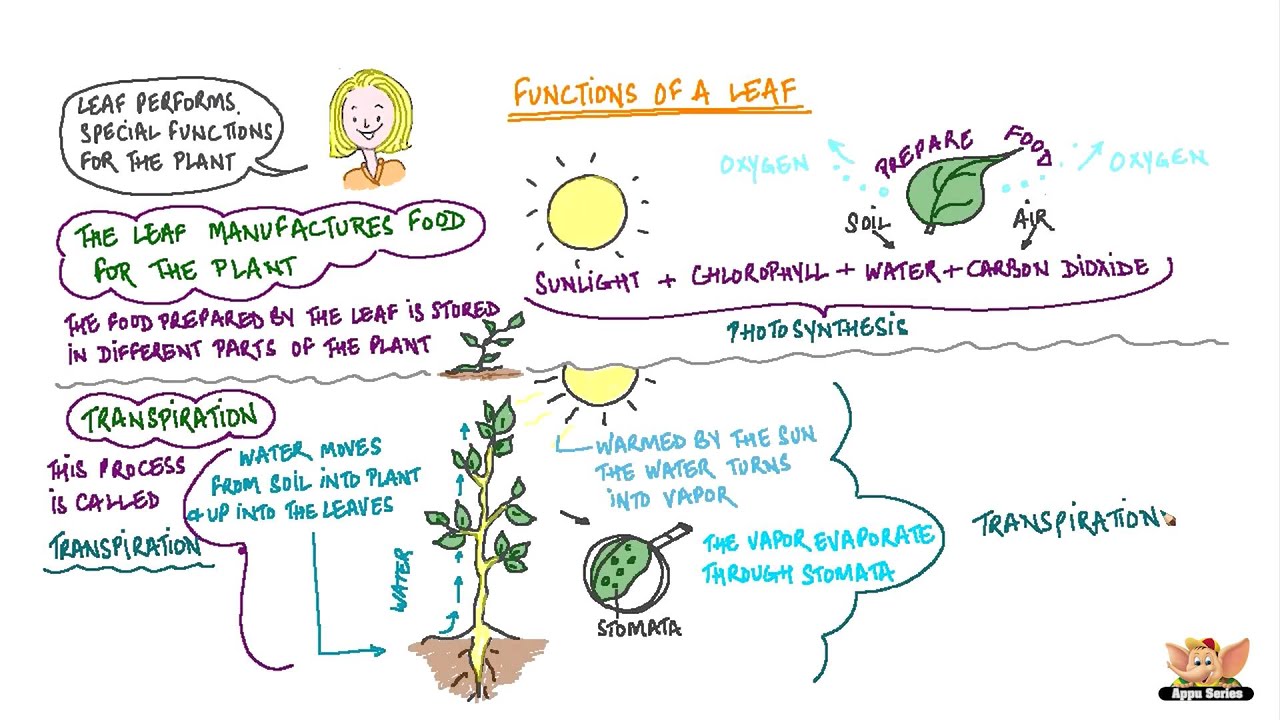
Quiz: Functions of Plant Parts. 1. The green pigment contained in plants is: A carotene B chlorophyll C chloroplast: 2. Photosynthesis is the process where plants convert: A sugar and sunlight into oxygen B sugar and oxygen into carbon dioxide and energy C carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen: 3. Water is taken from the surroundings into the plant through the: A leaves B stems C
4 Flower part Function Ovule carry female gametes after fertilisation, an ovule becomes a seed Stamen the MALE parts of a flower comprises an anther and a filament a filament holds an anther an anther holds the pollen grains to make pollen grains Carpel the FEMALE parts of a flower also known as pistil comprises stigma, style and ovary stigma is the sticky part that catch pollen grains during
Root, stem, flower, leaf! In this hands-on science lesson, your students will create their own plants to help them identify and remember the parts of a plant.
Flowers are the reproductive part of most plants. Flowers contain pollen and tiny eggs called ovules. After pollination of the flower and fertilization of the ovule, the ovule develops into a fruit. Flowers contain pollen and tiny eggs called ovules.
have many parts that play a role in fertilization, which results in fruit and seed production. Seeds are the Seeds are the reproductive structures of the plant.
The four main parts of a flower are generally defined by their positions on the receptacle and not by their function. Many flowers lack some parts or parts may be modified into other functions and/or look like what is typically another part. In some families, like – origami rose bouquet instructions Plant Cell Parts and Functions (Interactive Tutorial) 1. A guide to plant cell organelles . Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial. The cell wall. Part 1 is the cell wall. Cell
The receptacle is the part of the branch on which a flower forms. Color the receptacle (B) brown. Sepals are leaf like structures that surround and protect the flower before it blooms. Color the sepals (C) green. Petals are the colorful part of the flower that attracts insects and even other small
The parts and functions of a flower are much more detailed than they might appear at first glance. If you look at a flower from the top, you will be able to distinguish between four “whorls,” or circular sections that share a common center.
Anatomy of a Flower Super Teacher Worksheets
Flower Structure and Reproduction The Biology Corner
Parts of the flower and their functions Flashcards Quizlet
Parts of the Flower & their Functions mssuesbloq.typepad.com

The Functions of the Parts of a Flower Primary Resources
Flower Structure Functions of Flower Parts

crochet mini flower string tutorial 115 –
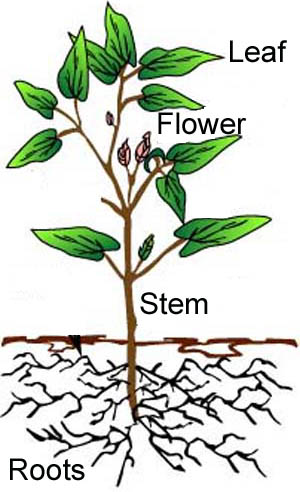

Describe the Parts of Flowers Sciencing
Flower Structure and Reproduction The Biology Corner
Root, stem, flower, leaf! In this hands-on science lesson, your students will create their own plants to help them identify and remember the parts of a plant.
Flowers are the reproductive part of most plants. Flowers contain pollen and tiny eggs called ovules. After pollination of the flower and fertilization of the ovule, the ovule develops into a fruit. Flowers contain pollen and tiny eggs called ovules.
Functions and Parts of a Plant (PDF) – Have fun learning about the lifecycle of a plant, including how flowers form and their various parts. Guide to Flowers (PDF) – Check out this cool flower picture guide that you can use to identify different parts of a flower once you learn about basic plant anatomy!
27/12/2011 · flower: A modified and condensed shoot useful for reproduction in angiosperms is called flower. Famous scientists like Linnaeus, Gaspard Bauhin, Goethe, de Candolle described flower as a …
The important parts of a flower and their specific functions have been listed in this article. The most important parts are its male and female parts, the carpel, and the stamen.
Quiz: Functions of Plant Parts. 1. The green pigment contained in plants is: A carotene B chlorophyll C chloroplast: 2. Photosynthesis is the process where plants convert: A sugar and sunlight into oxygen B sugar and oxygen into carbon dioxide and energy C carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen: 3. Water is taken from the surroundings into the plant through the: A leaves B stems C
The three primary parts of a seed are the embryo, endosperm, and seed coat. The embryo is the young multicellular organism before it emerges from the seed. The endosperm is a source of stored food, consisting primarily of starches. The seed coat consists of one or more protective layers that encase the seed. A seed begins to form an embryo following fertilization and the start of a zygote. The
Describe the Parts of Flowers Sciencing
Four Whorls The Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
Functions and Parts of a Plant (PDF) – Have fun learning about the lifecycle of a plant, including how flowers form and their various parts. Guide to Flowers (PDF) – Check out this cool flower picture guide that you can use to identify different parts of a flower once you learn about basic plant anatomy!
Quiz: Functions of Plant Parts. 1. The green pigment contained in plants is: A carotene B chlorophyll C chloroplast: 2. Photosynthesis is the process where plants convert: A sugar and sunlight into oxygen B sugar and oxygen into carbon dioxide and energy C carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen: 3. Water is taken from the surroundings into the plant through the: A leaves B stems C
Their parts are called the root, stem, branch, leaf, flower, fruit, and seed. We learned that roots anchor the plant to take in their water and nutrients and hold the plant firmly in the ground. Roots are also absorbers of water and minerals from the soil.
All flowers have male and female parts carpel stamen This is the name for the FEMALE part of the flower. This is the name for the MALE part of the flower. This is the name for the MALE part of the flower.
The parts of a plant and their functions 1. The Parts of a Plant and their Functions By: Elisabeth D.S. Cecil Nur A. Irfan Fahrizza Risngo Nanny B. Clementinus Ken B.
Flower Parts Strand Life parts and their functions. Extensions and Connections (for all students) If students used a digital camera to collect pictures of plants on the school grounds, the class book about plants could be produced electronically. Have students create a flip book with illustrations of the stages of pollination. Give four 3 x 5 inch index cards to each student, and have them
The Functions of the Parts of a Flower. ANTHER Female part, sticky and collects the pollen. CARPEL Male part, holds up the anther. FILAMENT Female part, tube that the pollen travels down.
This ‘ideal’ flower shows the basic parts of a flower. Children need to recognise these parts in Children need to recognise these parts in different flowers and understand their role or function in flowering plant reproduction.
The receptacle is the part of the branch on which a flower forms. Color the receptacle (B) brown. Sepals are leaf like structures that surround and protect the flower before it blooms. Color the sepals (C) green. Petals are the colorful part of the flower that attracts insects and even other small
Day One: Distribute Parts of a Flower (Handout One). Ask the learners to label the parts of the plant with the appropriate name and function. Ask learners to share their prior knowledge of plants. Correct or enhance their understanding as necessary. During this discussion, the teacher can begin to state possible analogies of the parts of a plant to the parts in government. (constitution is
Plant Cell Parts and Functions (Interactive Tutorial) 1. A guide to plant cell organelles . Many plant cell organelles are also found in animal cells. In what follows, I’ll focus on the parts unique to plants, and list the name and function of those organelles shared by both kingdoms. For an overview of animal cells, see the previous tutorial. The cell wall. Part 1 is the cell wall. Cell
Root, stem, flower, leaf! In this hands-on science lesson, your students will create their own plants to help them identify and remember the parts of a plant.
The flower has both female parts, called the pistil, and male parts, called the staemens. They work together to fertilize the plant and produce seeds. The petals of a flower attract other insects such as butterflies and bees to the plant to pollinate them.
Describe the Parts of Flowers Sciencing
Four Whorls The Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
Day One: Distribute Parts of a Flower (Handout One). Ask the learners to label the parts of the plant with the appropriate name and function. Ask learners to share their prior knowledge of plants. Correct or enhance their understanding as necessary. During this discussion, the teacher can begin to state possible analogies of the parts of a plant to the parts in government. (constitution is
have many parts that play a role in fertilization, which results in fruit and seed production. Seeds are the Seeds are the reproductive structures of the plant.
This ‘ideal’ flower shows the basic parts of a flower. Children need to recognise these parts in Children need to recognise these parts in different flowers and understand their role or function in flowering plant reproduction.
27/12/2011 · flower: A modified and condensed shoot useful for reproduction in angiosperms is called flower. Famous scientists like Linnaeus, Gaspard Bauhin, Goethe, de Candolle described flower as a …
Non-reproductive parts of a flower are known as the Perianth and consist of the petals, sepals and the nectary. Petals are usually the colored parts of the flower, although some flowers have specialized leaves called bracts that can be even more colorful than the flower itself.
Flower Parts Strand Life parts and their functions. Extensions and Connections (for all students) If students used a digital camera to collect pictures of plants on the school grounds, the class book about plants could be produced electronically. Have students create a flip book with illustrations of the stages of pollination. Give four 3 x 5 inch index cards to each student, and have them
female parts of the flower, consisting of the stigma and the style
4 Flower part Function Ovule carry female gametes after fertilisation, an ovule becomes a seed Stamen the MALE parts of a flower comprises an anther and a filament a filament holds an anther an anther holds the pollen grains to make pollen grains Carpel the FEMALE parts of a flower also known as pistil comprises stigma, style and ovary stigma is the sticky part that catch pollen grains during
GWS parts of a flower curriculum Groundwork Somerville
Functions of Plant Parts Quiz Qld Science Teachers
The parts of the flowers SlideShare
Functions and Parts of a Plant (PDF) – Have fun learning about the lifecycle of a plant, including how flowers form and their various parts. Guide to Flowers (PDF) – Check out this cool flower picture guide that you can use to identify different parts of a flower once you learn about basic plant anatomy!
Functions of Plant Parts Quiz Qld Science Teachers
Flower Structure Functions of Flower Parts
The important parts of a flower and their specific functions have been listed in this article. The most important parts are its male and female parts, the carpel, and the stamen.
Parts of the Flower & their Functions mssuesbloq.typepad.com
The parts of the flowers SlideShare
The Functions of the Parts of a Flower Primary Resources
female parts of the flower, consisting of the stigma and the style
Flower Structure and Reproduction The Biology Corner
Flowers are the reproductive part of most plants. Flowers contain pollen and tiny eggs called ovules. After pollination of the flower and fertilization of the ovule, the ovule develops into a fruit. Flowers contain pollen and tiny eggs called ovules.
Anatomy of a Flower Super Teacher Worksheets
Flower Structure and Reproduction The Biology Corner
Parts of the flower and their functions Flashcards Quizlet
Root, stem, flower, leaf! In this hands-on science lesson, your students will create their own plants to help them identify and remember the parts of a plant.
Flower Structure Functions of Flower Parts
Describe the Parts of Flowers Sciencing
female parts of the flower, consisting of the stigma and the style
The Functions of the Parts of a Flower Primary Resources
IXL Identify plant parts and their functions 3rd grade
The parts of a plant and their functions 1. The Parts of a Plant and their Functions By: Elisabeth D.S. Cecil Nur A. Irfan Fahrizza Risngo Nanny B. Clementinus Ken B.
Science Curriculum Unit Planner SOL
Four Whorls The Parts of a Flower and Their Functions
Anatomy of a Flower Super Teacher Worksheets